Understanding the Link Between Weight and Type 2 Diabetes
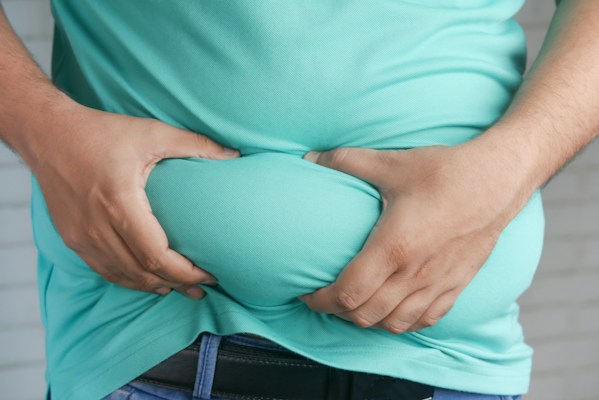
The intricate relationship between body weight and Type 2 diabetes is a crucial aspect of understanding and managing this widespread health condition. Excess weight, particularly around the abdominal area, is a significant risk factor for the development of Type 2 diabetes, highlighting the importance of weight management in both prevention and treatment strategies.
This article delves into the complex dynamics between excess weight and the onset of Type 2 diabetes, examining how factors like insulin resistance, lifestyle choices, and genetics intertwine. It also offers practical advice for effectively managing weight to mitigate the risk or impact of Type 2 diabetes.
Body Weight and Insulin Resistance
- Mechanism: Excess fat, especially visceral fat around the abdomen, leads to increased levels of fatty acids and inflammation. This can disrupt the function of insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels, leading to insulin resistance.
- Impact: Insulin resistance forces the pancreas to produce more insulin to keep blood sugar levels in check, eventually leading to Type 2 diabetes when the pancreas can no longer keep up.
Genetics and Lifestyle Factors
- Genetics: While genetics play a role in the development of Type 2 diabetes, lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity significantly influence its onset.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of physical activity, and being overweight are major risk factors. Even in individuals with a genetic predisposition, lifestyle changes can delay or prevent the onset of Type 2 diabetes.
The Role of Diet in Weight and Diabetes Management
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help maintain a healthy weight and regulate blood sugar levels.
- Portion Control: Understanding and controlling portion sizes can aid in weight loss and prevent blood sugar spikes.
Physical Activity: A Dual Benefit
- Weight Loss: Regular physical activity helps in weight loss, which can significantly reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Exercise enhances the body’s sensitivity to insulin, improving blood sugar management.
The Vicious Cycle of Obesity and Diabetes
- Cycle Explanation: Obesity increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes, and having Type 2 diabetes can make it more challenging to lose weight. High blood sugar levels can lead to increased hunger and fat storage.
- Breaking the Cycle: Effective management of diabetes and focused efforts on weight loss can help break this cycle.
Psychological Aspects of Weight and Diabetes
- Mental Health: Stress and depression are common in individuals struggling with weight and diabetes. These factors can make managing both conditions more challenging.
- Support Systems: Seeking support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or counseling can be beneficial in coping with these challenges.
Understanding and Managing Metabolic Syndrome
- Definition: Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- Relation to Diabetes: Individuals with metabolic syndrome have an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Weight management is key to reducing this risk.
Monitoring and Goal Setting
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels and weight is crucial in managing Type 2 diabetes.
- Goal Setting: Setting realistic weight loss goals and working towards them gradually can lead to better diabetes control.
Nutritional Education and Counseling
- Importance: Understanding the nutritional value of food and its impact on diabetes is vital. Nutritional counseling can provide personalized dietary advice.
- Action Plan: Consulting a dietitian or a diabetes educator can help in creating an effective diet plan.
Medication and Weight Management
- Medications: Some diabetes medications can result in weight gain. Discussing medication options with a healthcare provider is important.
- Balancing Act: Balancing medication with diet and exercise is crucial for effective diabetes and weight management.
The Importance of a Holistic Approach
- Comprehensive Management: Managing Type 2 diabetes and weight requires a holistic approach, including diet, exercise, medication, and mental health.
- Lifestyle Changes: Sustainable lifestyle changes are more effective than short-term diets or exercise fads.
In conclusion, understanding and addressing the link between weight and Type 2 diabetes is essential for effective disease management and prevention. This relationship underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy weight through balanced diet, regular physical activity, and informed lifestyle choices.
By actively managing weight, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing Type 2 diabetes or better control the condition if already diagnosed. This journey requires a holistic approach, encompassing not just physical health but also mental well-being and informed healthcare decisions. Ultimately, each step taken towards a healthier weight contributes to a stronger defense against the challenges of Type 2 diabetes.
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels is crucial in reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes, boosting energy, and enhancing overall life quality. These changes should be viewed as long-term commitments to a healthier lifestyle, rather than quick solutions. Individuals with Type 2 diabetes, by actively managing their weight, can take significant control of their health, paving the way for a more fulfilling and active life.