Navigating Weight Loss in Type 2 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide
For individuals with Type 2 diabetes, managing weight is not just about improving physical appearance; it’s a vital component of disease management and overall health. Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, is a key contributor to the development and progression of Type 2 diabetes, affecting insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of effective weight loss strategies for those with Type 2 diabetes. By focusing on sustainable lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and the importance of physical activity, we will explore how individuals can not only manage their condition more effectively but also enhance their overall well-being.
Understanding the Link Between Weight and Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes often develops in individuals with obesity or overweight. Excess fat, especially around the abdomen, can lead to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells don’t respond effectively to insulin. Losing weight can improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood glucose levels, and reduce the risk of complications.
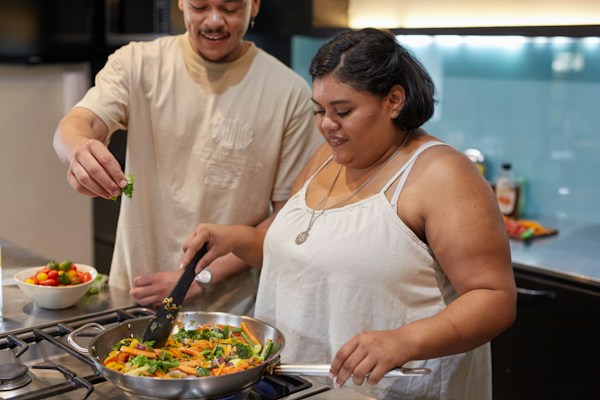
Dietary Changes for Weight Loss:
- Carbohydrate Management: Carbs have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels. Focus on low-glycemic index foods, which cause a slower, more gradual rise in blood sugar. Include whole grains, legumes, and plenty of non-starchy vegetables.
- Portion Control: Reducing portion sizes can help manage calorie intake, crucial for weight loss. Using smaller plates, checking serving sizes, and being mindful of hunger cues can help.
- Balanced Nutrient Intake: Ensure a balanced intake of macronutrients. Incorporate lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates into meals for satiety and nutrition.
Exercise for Weight Loss and Insulin Sensitivity: Physical activity is vital in managing Type 2 diabetes and losing weight. Exercise helps burn calories and increases insulin sensitivity.
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling help burn calories and control blood sugar.
- Resistance Training: Building muscle mass helps improve metabolic rate and insulin sensitivity. Weight lifting or bodyweight exercises can be effective.
Behavioral Strategies:
- Self-Monitoring: Keeping a food diary or using a digital app can help track food intake and identify patterns.
- Stress Management: Stress can affect blood sugar levels and eating habits. Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
- Adequate Sleep: Poor sleep can disrupt appetite-regulating hormones, leading to weight gain. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
Medical and Professional Support:
- Consulting Healthcare Providers: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers can help monitor progress and adjust medications as needed.
- Diabetes Education and Support Groups: Participating in diabetes education programs and support groups can provide valuable information and emotional support.
Understanding Natural Enzymes and Blood Glucose Management: Incorporating natural enzymes into your diet can play a significant role in managing blood glucose levels. Unlike These enzymes can improve digestion and nutrient absorption, potentially enhancing insulin sensitivity. It’s important to discuss with healthcare providers the integration of natural enzymes into your diabetes management plan, ensuring they complement your overall treatment strategy without risking hypoglycemia. This holistic approach can support weight loss goals and contribute to better blood glucose control.
Regular Monitoring of Blood Glucose Levels: Regular blood sugar monitoring helps understand how different foods and activities affect blood sugar levels. This can guide dietary and exercise choices.
Sustainable Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss in the context of Type 2 diabetes is not about fad diets but sustainable lifestyle changes. It’s about creating a healthy relationship with food and incorporating physical activity into daily routines.
In conclusion, managing weight effectively plays a pivotal role in controlling Type 2 diabetes. Adopting a balanced approach that encompasses dietary changes, regular physical activity, and behavioral modifications can lead to significant improvements in blood glucose levels and overall health.
Achieving and maintaining normal blood glucose levels reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications, enhances energy levels, and improves quality of life. It’s important to remember that these changes are not just short-term fixes but lifelong commitments to a healthier lifestyle. By taking proactive steps towards weight management, individuals with Type 2 diabetes can regain control over their health and lead fuller, more active lives.
** Please note ** the information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. I am not a doctor, and the recommendations made here should not replace professional medical guidance. Before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have Type 2 diabetes or any other health condition, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider. They can offer personalized advice and ensure that any new exercise routine is safe and appropriate for your individual health needs.