Navigating Rising Healthcare Costs in Retirement: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Escalating Healthcare Costs
The rising cost of healthcare in retirement is a significant concern, driven by several key factors. Technological advancements in medical care, while improving treatment quality, have led to increased expenses. These innovations, ranging from new procedures to advanced medical equipment, often come with a higher cost, impacting retirees who typically rely on fixed incomes.
Furthermore, longer life expectancies mean retirees require medical care over an extended period, leading to higher cumulative healthcare costs. This longer lifespan, a testament to medical progress, brings with it the reality of prolonged healthcare needs.
Adding to this financial strain is the growing prevalence of chronic diseases among the aging population. Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and arthritis necessitate ongoing management, including regular medications and doctor visits, which cumulatively contribute to the increasing healthcare budget in retirement.
These factors combined make healthcare one of the largest expenses for retirees. Managing these costs effectively is crucial and involves understanding medical benefits, insurance options, and engaging in proactive health management. For retirees, addressing these healthcare expenses is essential for maintaining financial stability and ensuring a quality life in their later years. Key steps for managing healthcare costs include getting to know Medicare benefits and looking into extra health insurance to make sure you have a secure and healthy retirement.
Medicare: The Foundation of Retiree Healthcare
Medicare is the federal health insurance program for people aged 65 and older in the United States. Understanding its structure is crucial for retirees:
- Medicare Part A (Hospital Insurance): Covers inpatient hospital stays, care in a skilled nursing facility, hospice care, and some home health care. Most people don’t pay a monthly premium for Part A if they have paid Medicare taxes while working.
- Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance): Covers certain doctors’ services, outpatient care, medical supplies, and preventive services. Part B requires a monthly premium.
- Medicare Part C (Medicare Advantage Plans): A type of Medicare health plan offered by private companies that contract with Medicare to provide Part A and Part B benefits. These plans often include Part D and additional services, with varying costs.
- Medicare Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage): Helps cover the cost of prescription drugs and may lower your drug costs and protect against higher costs in the future.
Gaps in Medicare Coverage
While Medicare provides broad coverage, it does not cover everything. There are gaps that retirees need to be aware of:
- Deductibles and Co-pays: Medicare requires deductibles and co-pays for services, which can add up over time.
- Long-Term Care: Medicare generally does not cover long-term care costs like nursing home care or the full cost of custodial care.
- Dental, Vision, and Hearing: These are not typically covered under standard Medicare plans.
- Prescription Drugs: While Part D covers prescription drugs, it does not cover all medications, and there may be significant out-of-pocket costs.
Supplemental Health Insurance: Bridging the Gaps
To manage the costs that Medicare does not cover, many retirees opt for supplemental health insurance plans. These include:
- Medigap: Private insurance policies that pay after Medicare pays and are designed to cover some or all of the expenses not covered by Medicare.
- Medicare Advantage Plans (Part C): These plans often provide extra coverage, such as vision, hearing, dental, and/or health and wellness programs. They may also include Medicare prescription drug coverage (Part D).
- Long-Term Care Insurance: Specifically designed to cover long-term care services, this insurance can be a significant asset for those who want to protect their savings against the high costs of long-term care.
Budgeting for Healthcare in Retirement
Planning for healthcare costs in retirement requires a proactive approach:
- Estimate Healthcare Costs: Use available tools and resources to estimate your healthcare costs in retirement, taking into account your current health, family medical history, and potential future healthcare needs.
- Consider Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): If you have a high-deductible health plan, contributing to an HSA can be a tax-advantaged way to save for healthcare costs in retirement.
- Review and Adjust Plans Annually: Healthcare needs can change annually; so should your Medicare and supplemental insurance plans. Regular reviews ensure you have the coverage you need at the best price.
Staying Healthy to Reduce Costs
One of the best ways to minimize healthcare costs in retirement is to stay healthy:
- Preventive Care: Take advantage of preventive services offered by Medicare and other health insurance plans.
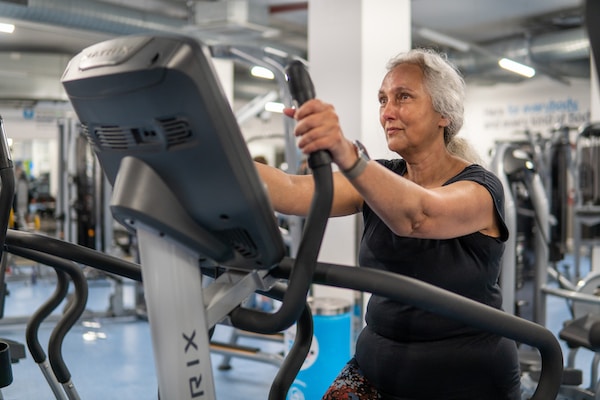
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Engaging in regular physical activity, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco can reduce the risk of chronic diseases and the associated healthcare costs.
Navigating the Complexities of Medicare and Supplemental Insurance
Understanding Medicare and the various supplemental insurance options can be complex. Consider the following:
- Educate Yourself: Take advantage of resources provided by the Medicare website, local seminars, and elder law attorneys specializing in Medicare.
- Professional Advice: Consulting with a financial advisor or a Medicare expert can provide clarity and help in making informed decisions.
Conclusion
Navigating the rising healthcare costs in retirement is a critical aspect of ensuring a secure and comfortable retirement. Understanding Medicare’s intricacies, coupled with the prudent selection of supplemental health insurance, can significantly alleviate the financial burden of medical expenses. By staying informed about the latest advancements in medical care, the implications of longer life expectancies, and the management of chronic diseases, retirees can make informed decisions that safeguard their health and finances.
The journey to a worry-free retirement in terms of healthcare is complex, but with the right knowledge and planning, it is certainly achievable. It’s about striking a balance between being prepared for healthcare costs and enjoying the golden years to the fullest. Remember, effective healthcare management in retirement is not just about covering costs; it’s about ensuring a quality of life that allows you to enjoy this new, exciting phase to its fullest potential.